Throughout history, certain events have altered the world in significant ways, reshaping societies, borders, economies, and the global balance of power. These turning points not only affected those who lived through them but also set the course for future generations. From political revolutions to scientific discoveries, these pivotal moments changed how people live, think, and interact with one another. This article explores some of the most influential historical events and the ways in which they have left a lasting impact on humanity.
The Fall of the Roman Empire
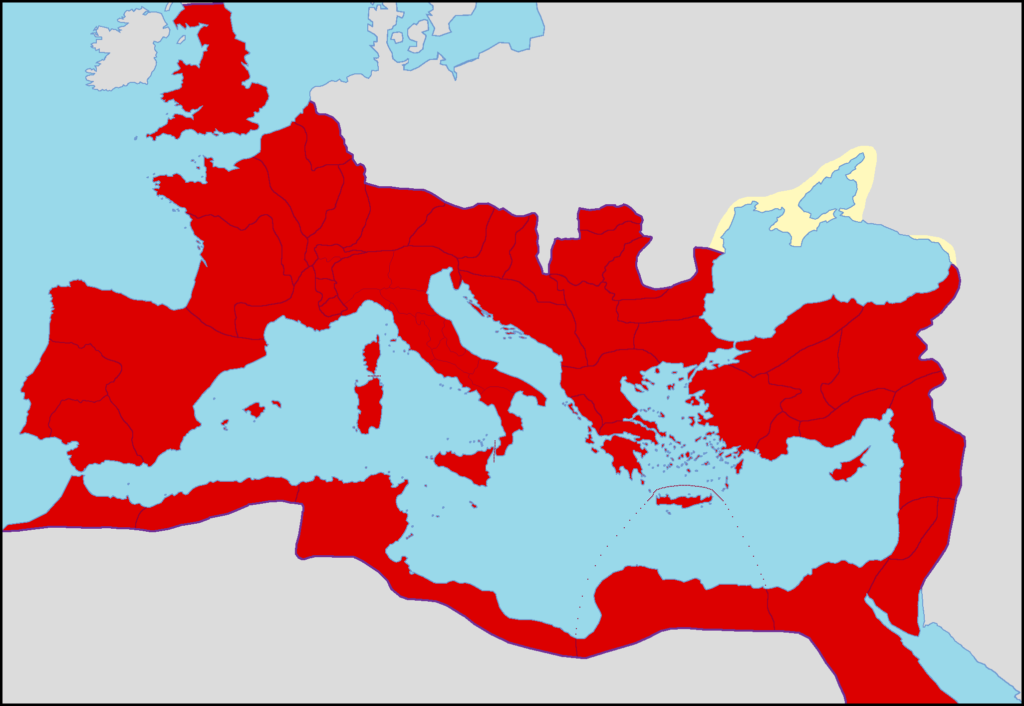
The fall of the Roman Empire in 476 CE marked the end of ancient civilization and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The decline of Rome’s vast empire, which stretched from Europe to North Africa and the Middle East, led to the fragmentation of Western Europe and created a power vacuum that would define the structure of the medieval world. Without centralized Roman rule, smaller kingdoms and local rulers rose to power, leading to the feudal system that characterized much of the Middle Ages. The fall also set the stage for the rise of Christianity as a unifying force in Europe, which would shape European culture and politics for centuries. The end of the Roman Empire highlighted the vulnerability of even the greatest empires and continues to serve as a lesson about the fragility of power.
The Discovery of the New World
Christopher Columbus’s discovery of the Americas in 1492 opened up a new chapter in human history, as Europe became aware of previously unknown continents. This discovery sparked an era of exploration, colonization, and global trade that profoundly reshaped societies on both sides of the Atlantic. Indigenous civilizations in the Americas faced dramatic changes as European settlers arrived, resulting in cultural exchanges, conflicts, and profound demographic shifts. The flow of goods, ideas, and people across the Atlantic is often referred to as the Columbian Exchange, which introduced new crops, animals, and technologies to various parts of the world. The discovery of the New World laid the foundation for the globalized world we live in today, influencing everything from trade to international relations.
The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, which began in Britain in the 18th century, transformed economies, societies, and daily life on an unprecedented scale. Before industrialization, most people lived in agrarian societies, working on farms and producing goods by hand. The advent of machinery and factories changed the nature of work, leading to urbanization as people moved to cities in search of jobs. Innovations in steam power, transportation, and manufacturing revolutionized industries and increased productivity, laying the groundwork for the modern economy. The Industrial Revolution also had profound social effects, as it created a new working class and led to the development of labor movements. Its influence on modern society is immense, from the way we work to the products we consume, making it one of history’s most impactful events.
The French Revolution
The French Revolution, which began in 1789, brought about sweeping social and political changes, not only in France but across Europe and beyond. Driven by Enlightenment ideas and economic hardship, the French people overthrew the monarchy, leading to the rise of republicanism and the end of feudal privileges. The revolution introduced ideas of liberty, equality, and fraternity, which influenced other nations and sparked similar revolutionary movements worldwide. Napoleon Bonaparte’s rise to power following the revolution brought these principles to many parts of Europe, altering traditional monarchies and inspiring future democratic reforms. The French Revolution remains a symbol of the fight for freedom and justice, inspiring social and political movements to this day.
The World Wars and Their Global Impact
The two World Wars in the 20th century were among the most destructive conflicts in history, reshaping nations and altering global dynamics. World War I led to the fall of empires and set the stage for major political and social changes, including the Russian Revolution and the eventual rise of communism. World War II, following closely on the heels of the first, was marked by unprecedented destruction and atrocities, leading to the establishment of the United Nations and a focus on international cooperation to prevent future conflicts. The post-World War II era also saw the emergence of the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union, influencing global alliances, politics, and military strategies for decades. The effects of these wars are still visible today, as they shaped borders, political ideologies, and international relationships.
The Rise of the Digital Age
The rise of the digital age, beginning in the latter half of the 20th century, has fundamentally transformed communication, commerce, and information exchange. The development of computers, the internet, and mobile technology created a world where people are more connected than ever before. This digital revolution has altered how businesses operate, how people learn, and how we interact with the world. The internet’s global reach has made it possible to access information instantly, reshaping fields like education, entertainment, and work. The digital age continues to evolve rapidly, influencing nearly every aspect of modern life and creating new opportunities and challenges for future generations.
Conclusion: History’s Impact on Modern Society
These historical events have each contributed to the shaping of the modern world, influencing everything from government systems and economic structures to cultural practices. They serve as reminders of the power of innovation, human resilience, and the consequences of our actions. Today, we celebrate traditions and exchange gifts, much like Diwali gifts, to honor shared values and history, connecting us to the past and inspiring hope for the future. As we reflect on these events, we are reminded that history is not just a record of the past but a force that continuously shapes our present and future. Understanding these turning points allows us to appreciate the interconnectedness of human experience and prepares us to face the challenges of tomorrow.






