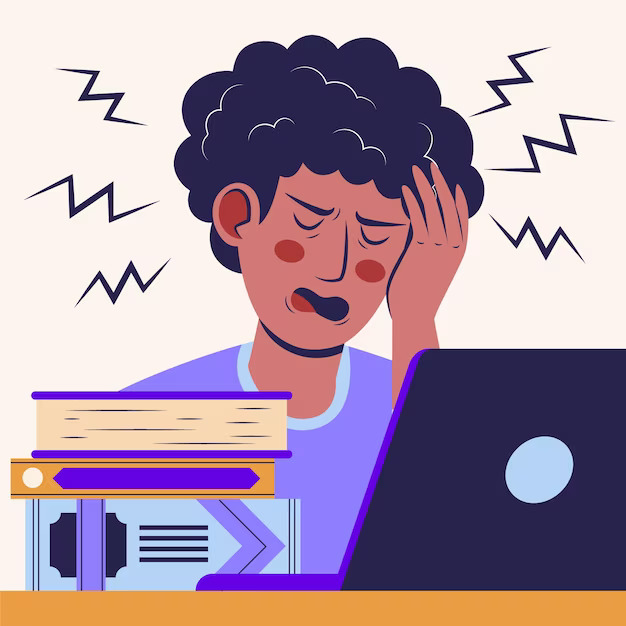
Social burnout is a condition characterized by exhaustion and overwhelms resulting from excessive social interaction and engagement. It occurs when individuals feel mentally and emotionally drained due to prolonged exposure to social activities, interactions, and obligations.
Social exhaustion can lead to decreased motivation, enjoyment, and increased social anxiety. Taking breaks, setting boundaries, and practicing self-care are essential in managing and preventing Social overload. People experiencing social burnout often feel overwhelmed, and fatigued, and find it challenging to cope with social demands.
What does social burnout look like?
Social burnout manifests as a feeling of overwhelming exhaustion and detachment from social interactions and activities. Individuals experiencing social burnout may withdraw from social events, feel irritable or disconnected when around others, and struggle to maintain relationships. They may also experience physical symptoms such as fatigue, headaches, or changes in appetite or sleep patterns. Social burnout can result from prolonged exposure to social stressors, excessive demands on one’s time and energy, or feeling overwhelmed by social expectations.
What Causes Social Burnout?
For those suffering from social burnout, seeking support through “Therapy near me” can provide much-needed assistance and guidance.
- Excessive socializing: Spending too much time engaging in social activities can overload an individual’s capacity to handle social interactions.
- High social expectations: Feeling pressured to meet societal or peer expectations regarding socializing and maintaining a busy social calendar.
- Social media overload: Constantly being connected to social media platforms and feeling the need to constantly engage and respond to updates and notifications.
- Lack of alone time: Not having enough time for solitude and personal reflection can lead to Social overload.
- Emotional labor: Consistently having to manage and regulate emotions during social interactions, such as in customer service or caregiving roles.
- Social comparison: Frequent comparison of oneself to others on social media platforms or in real-life social settings can contribute to feelings of inadequacy and burnout.
- Overcommitment: Taking on too many social obligations, such as attending numerous events or parties, can lead to exhaustion and burnout.
- People-pleasing tendencies: Constantly trying to please others and meet their expectations can be emotionally draining.
- Lack of boundaries: Failing to set clear boundaries in social relationships can lead to feelings of overwhelm and burnout.
- Conflict and drama: Being consistently exposed to conflicts, disagreements, and drama within social circles can be mentally and emotionally exhausting.
- Social anxiety: Experiencing anxiety and stress in social situations can contribute to Social exhaustion.
- Introversion and extroversion mismatches: For introverts, excessive socializing can drain energy, while extroverts may experience burnout from not having enough social interaction.
- Social pressure to be always available: Feeling the need to be constantly accessible and responsive to others’ social demands can lead to burnout.
It’s important to note that individual experiences may vary, and a combination of these factors can contribute to social burnout in different people.
What Are the Risks of Social Burnout?
Experiencing social burnout can pose several risks to an individual’s well-being, highlighting the importance of seeking “Anxiety counselling” support. Here are that highlight the potential risks associated with social burnout:
- Mental and emotional exhaustion: Social depletion can lead to a state of chronic fatigue, making it difficult to cope with daily life and responsibilities.
- Decreased productivity: The exhaustion and overwhelm from social burnout can negatively impact an individual’s ability to focus and perform tasks effectively.
- Impaired social functioning: Social overload can hinder one’s ability to engage in healthy social interactions, leading to strained relationships and a decline in social skills.
- Increased social anxiety: Burnout can intensify feelings of social anxiety, making it more challenging to engage in social situations comfortably.
- Negative impact on mental health: Social weariness can contribute to the development or exacerbation of mental health issues, such as depression or anxiety disorders.
- Decreased motivation and enjoyment: Burnout can diminish one’s enthusiasm and pleasure in social activities that were once enjoyable.
- Feelings of isolation and loneliness: Social burnout may lead to withdrawal and isolation, resulting in a sense of loneliness and disconnection from others.
- Physical health consequences: Prolonged burnout can impact physical health, including weakened immune function, sleep disturbances, and increased susceptibility to illnesses.
- Increased stress levels: Social fatigue can contribute to elevated stress levels, which can have detrimental effects on both mental and physical health.
- Impaired decision-making: Exhaustion and overwhelm from burnout can hinder an individual’s ability to make sound judgments and decisions.
- Reduced self-esteem: Social fatigue can undermine self-confidence and self-worth, leading to feelings of inadequacy or self-doubt.
- Neglected self-care: When overwhelmed by Social tiredness, individuals may neglect their own self-care and well-being.
- Increased risk of burnout in other areas of life: Social fatigue can spill over into other aspects of life, such as work or personal relationships, increasing the risk of burnout in those areas as well.
- Limited personal growth: Burnout can impede personal development and hinder opportunities for learning and growth within social contexts.
conclusion
It’s important to recognize the risks associated with social burnout and take proactive steps to prevent and manage it in order to maintain a healthy balance in social interactions and overall well-being.